Title: Unveiling NVIDIA’s Three-Computer Solution for Robotics: A Game-Changing Approach
In the rapidly evolving landscape of robotics, NVIDIA continues to push the boundaries of innovation, introducing groundbreaking technologies that are reshaping the future of this field. One such development is NVIDIA’s Three-Computer Solution for Robotics, a revolutionary system designed to enhance the performance, flexibility, and safety of robotic systems. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of this cutting-edge solution, exploring its components, benefits, and potential applications.
The Three-Computer Solution for Robotics is a system that consists of three interconnected computers: the Jetson AGX Xavier for on-device AI, the NVIDIA Xavier NX for edge computing, and the NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD for cloud-based AI. By combining the strengths of these powerful computers, NVIDIA aims to address the challenges of real-time AI processing, edge computing, and cloud-based AI, thereby creating a robust, scalable, and flexible solution for robotics.
Join us as we journey through this exciting new frontier, exploring the potential of NVIDIA’s Three-Computer Solution for Robotics and its implications for industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare, transportation, and beyond. Whether you’re a robotics enthusiast, a tech-savvy professional, or simply curious about the latest advancements in AI and robotics, this article promises to provide valuable insights into a technology that is set to redefine the future of robotics.
Table of Contents
- Understanding NVIDIA’s Three-Computer Solution for Robotics: An Overview
- Breaking Down the Components: A Closer Look at NVIDIA’s Robotics Computing Architecture
- The Role of Jetson AGX Xavier in NVIDIA’s Robotics Solution: Power and Performance
- The Integration of NVIDIA’s Drive AGX Platform for Real-Time AI Processing in Robotics
- Optimizing Robotics Performance with NVIDIA’s Isaac Simulator and AI Workflow Suite: Recommendations for Successful Implementation
- Q&A
- The Conclusion
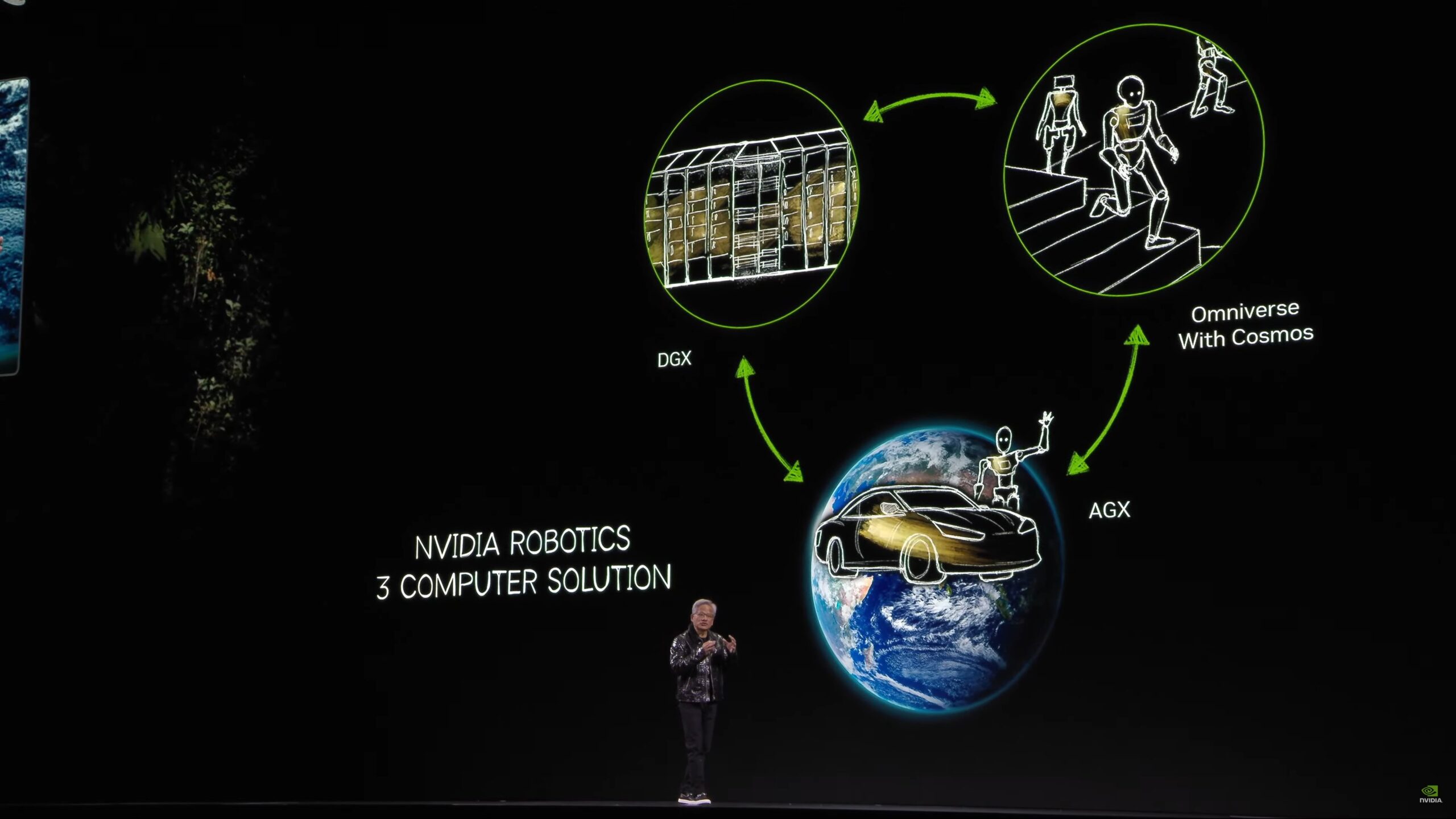
Understanding NVIDIA’s Three-Computer Solution for Robotics: An Overview
What Is NVIDIA’s Three-Computer Solution for Robotics?
In the ever-evolving world of robotics, NVIDIA’s Three-Computer Solution has emerged as a groundbreaking approach to powering AI-driven robots. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this innovative system.
The Core Components
- NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier: This powerful, compact module serves as the On-Board Computer for the robot. It’s equipped with eight-core ARM CPU, a 512-core Volta GPU, and a 64-tensor TFLOP AI accelerator, making it capable of handling complex AI tasks on the robot itself.
- NVIDIA Jetson TX2: Deployed as the Edge Computer, this device handles real-time data processing from the robot’s sensors. Its high-performance GPU and deep learning accelerator enable it to perform tasks such as object detection and classification.
- NVIDIA DGX Station or DGX-2: These high-performance Data Center Servers are used for offline training of AI models. They offer significant computational power, allowing for the development and refinement of advanced AI algorithms that can be deployed on the robot.
The Synergy
The Three-Computer Solution leverages the strengths of each component to create a robust and efficient AI system for robots. The on-board Jetson AGX Xavier manages real-time AI inference, while the edge Jetson TX2 processes sensor data. The data center servers, DGX Station or DGX-2, are used for training AI models offline, ensuring the robot can learn and adapt from vast amounts of data. This synergy enables robots to make quick, intelligent decisions, enhancing their performance and overall functionality.
Breaking Down the Components: A Closer Look at NVIDIA’s Robotics Computing Architecture
What Is NVIDIA’s Three-Computer Solution for Robotics?
In the realm of robotics, NVIDIA’s innovative computing architecture stands out as a game-changer. Let’s delve into the intricacies of NVIDIA’s three-computer solution, a groundbreaking approach designed to revolutionize robotics performance.
- Jetson AGX Xavier: Known as the “brain” of the system, this powerful AI supercomputer delivers 32 TOPS (TeraOps) of power, making it ideal for real-time, high-performance AI computation. With 512 CUDA cores, 57.6 GB/s memory bandwidth, and a dedicated 8-core ARM64 CPU, the Jetson AGX Xavier handles complex AI algorithms with ease.
- Jetson Nano: Serving as the “neck” of the system, the Jetson Nano acts as a bridge between the Jetson AGX Xavier and the peripherals. It provides a platform for developing and testing robotics applications before deploying them on the more powerful AGX Xavier. With 128 CUDA cores and 16 GB of LPDDR4 memory, the Jetson Nano offers a cost-effective solution for developing AI-powered robotics applications.
- DRIVE AGX Orin: The “spine” of the system, the DRIVE AGX Orin is a scalable AI computing platform designed for autonomous vehicles. With up to 288 TOPS of AI performance, it is more powerful than the AGX Xavier, making it ideal for high-performance, safety-critical applications. The DRIVE AGX Orin combines 104 Tensor Cores, 8-core ARM64 CPU, and 8GB of HBM2 memory to deliver unparalleled AI performance for autonomous vehicles and advanced robotics.
Together, these three computers form a robust, scalable, and powerful computing architecture that enables the development of AI-powered robots capable of complex tasks, learning, and adaptability. This three-computer solution from NVIDIA is set to redefine the future of robotics, paving the way for smarter, more capable, and more efficient robots.
The Role of Jetson AGX Xavier in NVIDIA’s Robotics Solution: Power and Performance
The Powerhouse: Jetson AGX Xavier in NVIDIA’s Robotics Solution
At the heart of NVIDIA’s three-computer solution for robotics lies the Jetson AGX Xavier, a high-performance AI computing module designed specifically for edge computing in robotics, autonomous machines, and embedded systems.
Key Features of Jetson AGX Xavier
- Raw Power: Jetson AGX Xavier delivers 30 TOPS (TeraOps) of AI performance, making it 10x more powerful than its predecessor, Jetson TX2.
- Efficiency: With a power-efficient 55W design, Jetson AGX Xavier can handle complex AI tasks while minimizing power consumption, ensuring uninterrupted operation in robotics applications.
- AI at the Edge: Jetson AGX Xavier’s AI capabilities enable real-time AI processing at the edge, reducing latency and improving responsiveness in robotics applications.
Performance in Action
In the realm of robotics, Jetson AGX Xavier’s performance translates into powerful capabilities such as:
- Real-time Object Detection: Accurate object detection and recognition in real-time, enhancing robot autonomy and interaction with the environment.
- Deep Learning Inference: Rapid inference of deep learning models, enabling robots to learn and adapt to new situations quickly.
- Computer Vision: Advanced computer vision capabilities for tasks such as image and video processing, object tracking, and 3D modeling.
By harnessing the power of Jetson AGX Xavier, NVIDIA’s three-computer solution for robotics offers a robust, high-performance platform for developers to create intelligent, autonomous machines that can navigate, learn, and interact with the world around them.
The Integration of NVIDIA’s Drive AGX Platform for Real-Time AI Processing in Robotics
Understanding NVIDIA’s Three-Computer Solution for Robotics
In the rapidly evolving world of robotics, NVIDIA’s Drive AGX platform stands out as a game-changer for real-time AI processing. At the heart of this solution is a three-computer architecture designed to optimize performance, flexibility, and scalability.
The Components
– Xavier AGX: This is the primary AI computing engine. Based on NVIDIA’s custom-built Xavier SoC, it delivers 30 trillion operations per second (TOPS) of AI performance. It’s responsible for running the most demanding AI workloads, such as perception, planning, and control.
– Pegasus: This is a high-performance computing server, designed to offload tasks that don’t require real-time processing, such as map processing, simulation, and learning. With up to 16 NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPUs, Pegasus can handle massive data sets and complex computations.
– Orin: The future-proof component, Orin is an upcoming SoC from NVIDIA, promising even higher AI performance than Xavier AGX. It’s designed to take over as the primary AI computing engine in future iterations of the Drive AGX platform.
The Synergy
The integration of these three components creates a powerful system that can handle both the complex real-time AI processing required by robots and the large-scale, non-real-time computations needed for tasks like map processing and learning. By offloading non-real-time tasks to Pegasus, Xavier AGX can focus on the immediate needs of the robot, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
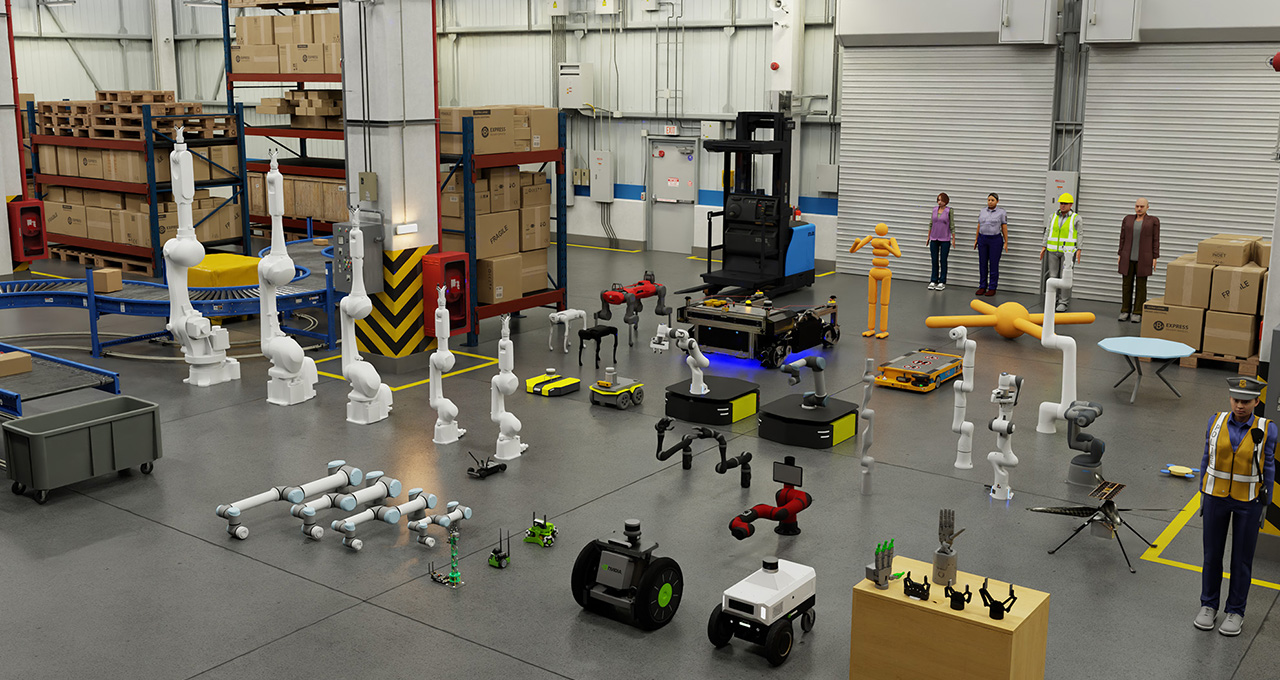

Optimizing Robotics Performance with NVIDIA’s Isaac Simulator and AI Workflow Suite: Recommendations for Successful Implementation
Unveiling NVIDIA’s Three-Computer Solution for Robotics
In the realm of robotics, NVIDIA’s Isaac Simulator and AI Workflow Suite have become indispensable tools for optimizing performance and streamlining the development process. One of the most intriguing aspects of NVIDIA’s solution is the three-computer setup, designed to provide a robust and efficient environment for robotics development.
The Three-Computer Setup
- Computer 1: This is the main development machine, equipped with NVIDIA’s RTX GPUs, which run the Isaac Simulator and AI Workflow Suite. It is responsible for simulating the robot’s environment, training AI models, and developing robotics applications.
- Computer 2: This is the edge compute device, which is typically a Jetson AGX Orin or Jetson Xavier NX. It is deployed on the robot itself and executes the trained AI models in real-time, allowing the robot to make decisions based on its environment.
- Computer 3: This is the cloud server, used for data storage, analytics, and remote monitoring. It can be accessed from the main development machine, allowing developers to analyze data, debug issues, and monitor the robot’s performance remotely.
By utilizing this three-computer solution, developers can effectively separate the development, training, and real-time execution of AI models, resulting in a more efficient and streamlined robotics development process.
Key Recommendations for Successful Implementation
- Optimize Simulation: Ensure that the Isaac Simulator is configured to accurately replicate the robot’s environment, as this will significantly improve the effectiveness of AI model training.
- Use GPU-Accelerated Training: Leverage the power of NVIDIA’s GPUs for AI model training to reduce training times and improve model performance.
- Secure Remote Access: Implement secure remote access to the cloud server to ensure data privacy and allow for efficient monitoring and debugging of the robot’s performance.
By following these recommendations and harnessing the power of NVIDIA’s three-computer solution, you can optimize your robotics performance and accelerate your development process. Embrace the future of robotics with NVIDIA’s Isaac Simulator and AI Workflow Suite!
Q&A
Title: Unveiling NVIDIA’s Three-Computer Solution for Robotics: A Comprehensive Guide
Q1: What is NVIDIA’s three-computer solution for robotics, and why is it significant?
A1: NVIDIA’s three-computer solution for robotics, known as the Jetson AIoT (Internet of Things) platform, is a powerful and integrated system designed to accelerate the development and deployment of AI-powered robots. The significance of this solution lies in its ability to streamline the process of building robots, making it easier for developers to create intelligent machines that can perform tasks more efficiently and effectively.
Q2: What are the three computers that make up NVIDIA’s solution, and what roles do they play?
A2: The three computers in NVIDIA’s solution are the Jetson Nano, the Jetson AGX Xavier, and the Jetson TX2. The Jetson Nano serves as the edge device, handling real-time computations and processing data close to the source. The Jetson AGX Xavier is a high-performance AI supercomputer for robots, capable of handling complex AI tasks such as object recognition and navigation. Lastly, the Jetson TX2 acts as a flexible and powerful computing platform, suitable for applications that require a balance between power and cost.
Q3: How does the Jetson AIoT platform facilitate the development of AI-powered robots?
A3: The Jetson AIoT platform provides developers with a comprehensive toolkit for building AI-powered robots. It offers advanced software libraries and tools, such as the NVIDIA Isaac SDK, which simplifies the process of integrating AI, perception, and control for robotics applications. Additionally, the platform supports popular robot operating systems like ROS (Robot Operating System) and MOOS (Mission Oriented Operating Suite), enabling seamless integration with existing robotics infrastructure.
Q4: What are some examples of applications where NVIDIA’s three-computer solution could be beneficial?
A4: NVIDIA’s three-computer solution can be applied in a wide range of industries and applications, including manufacturing, logistics, agriculture, healthcare, and service robotics. For instance, in manufacturing, robots equipped with this solution could perform tasks such as inspection, assembly, and packaging more efficiently and accurately. In agriculture, they could automate tasks like crop monitoring, harvesting, and irrigation, helping to increase productivity and reduce labor costs.
Q5: How does NVIDIA’s three-computer solution contribute to the advancement of AI and robotics?
A5: By providing an integrated and powerful platform for developing AI-powered robots, NVIDIA’s three-computer solution is driving innovation in the field of AI and robotics. It enables developers to create more intelligent, agile, and adaptable robots that can perform a wider range of tasks, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in robotics and AI. This, in turn, could lead to significant improvements in various industries and contribute to the development of a more automated and efficient future.
The Conclusion
Title: Wrapping Up: NVIDIA’s Three-Computer Solution for Robotics
In conclusion, NVIDIA’s three-computer solution for robotics, comprising Jetson AGX Xavier for on-device AI processing, Jetson Orin for edge AI and high-performance computing, and the NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD for cloud-based AI, represents a significant leap forward in the realm of robotics. This innovative architecture empowers developers to create more capable, efficient, and intelligent robots.
By offloading computationally intensive tasks to the Jetson AGX Xavier and Jetson Orin, robots can make real-time decisions based on sensor data, ensuring seamless interaction with their environment. Meanwhile, the NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD provides the necessary scalability and power for large-scale simulations, data analysis, and AI model training.
This trio of computers not only accelerates the development and deployment of robots but also paves the way for a future where robots are ubiquitous, autonomous, and capable of performing a wide range of tasks, from manufacturing to healthcare, and beyond. As we continue to witness advancements in AI and robotics, NVIDIA’s three-computer solution is poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of these technologies.
Stay tuned for more insights into the world of AI and robotics, as we explore the latest trends, innovations, and applications that are transforming industries and our daily lives. Until next time, happy learning!


Recent Comments